Currently there is world-wide interest in the song “Soon May The Wellerman Come”. Social media is simply heaving with shanty mania. There is of course a Dunedin connection and a recent article in the Otago Daily Times explains the history of the Weller Brothers shore whaling station at Ōtākou and a little bit of background on the origin of the song. https://www.odt.co.nz/news/dunedin/wellerman-sea-shanty-global-hit
The song includes the line “And bring us sugar and tea and rum,” referring to essential treats distributed regularly to the whaling gangs employed by the Weller Brothers. This reminded me I had seen many references to sugar, tea and rum in of one of our most significant archival collections – the Octavius Harwood papers.
The Harwood papers are probably the best collection of archives still extant from a shore whaling station in New Zealand. Octavius Harwood was employed late in 1837 to run the store and oversee some of the station’s activities and he kept extensive records that were preserved by later generations of his family and eventually came to the Hocken in the 1930s with the papers of George Craig Thomson.
Octavius Harwood’s journals describe what life was like for those working in the 1830s whaling industry around Ōtākou and the Otago coastline. With our help from current HUMS 201 intern, Caitlyn Duff, I have transcribed and edited an extract from the start of Harwood’s 1838 journal.
To make the extract more readable I expanded abbreviations and corrected spelling to modern spelling and removed some capitals. I also used square brackets to annotate some terms and names in the text.
The close relationship of Māori and European working together in the settlement of Ōtākou is clear in the journal with regular reference to the work Māori did at the station and in the whale fisheries. Many whalers, including Harwood and his employer Edward Weller married local women and an extensive network of whānau was created along the Otago coast.

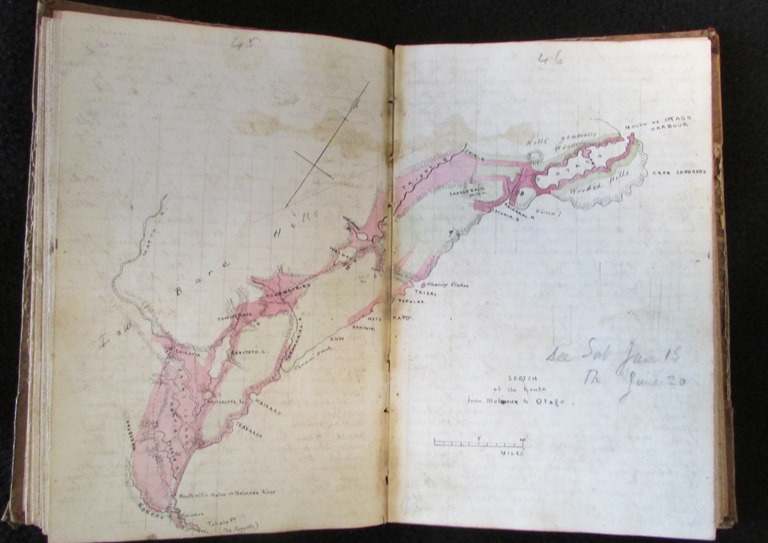
Harwood’s original journal commencing in 1838, MS-0438/001 Hocken Collections Uare Taoka o Hākena
The original journal is hand sewn, probably by Harwood himself and bears the stains and scuffs of a hard life at the store. It is made of Downton Mill paper water marked 1834.
Harwood supplied provisions to the whaling gangs, who visited Ōtākou to pick up their supplies. The gangs picked up two or so weeks’ worth of supplies and dropped off the prepared oil and bone. On one occasion in this extract Taiaroa and Karetai delivered some supplies from Harwood’s store to the nearby Pūrākaunui whaling station.
The supplies almost always consisted of sugar, tea, grog (a rum and water mix), tobacco, flour and sometimes casks of salted beef or pork. Whaling gear – rope, tools, casks or shooks (supplies for barrel making) and slops (cheap cotton canvas clothing) were also often supplied. Occasionally spirits were supplied to the whaling gang leaders. There seemed to be little fresh food distributed, perhaps the gangs supplemented their diet by trading locally, fishing, hunting and gathering.
The ship Dublin Packet was at Ōtākou at the time and Harwood spent much time unloading supplies and loading oil and bone on the ship. He also supplied a visiting French whaling ship.
Harwood supervised the cooper (barrel maker) at Ōtākou, and a team of usually six Māori who cleaned whalebone, and did other work such as building repairs, road repairs and fencing. He sometimes pickled pork in barrels and purchased potatoes from Māori.
He also issued provisions for “the House” – presumably the house where Edward Weller lived. Weller’s activities are mentioned occasionally. Edward eventually returned to live in Sydney when the business failed and further archival records of the Weller Brothers business are held at the State Library of New South Wales in Sydney, where they have been digitised and are available online. http://archival.sl.nsw.gov.au/Details/archive/110364025?_ga=2.66028653.2102099567.1611630649-263552842.1611630649
THE JOURNAL
1838
April 24th. – Received from the Dublin Packet a quantity of rope – Whale line – Grass rope – flour in casks – Boat planks – Chests tea – Cans oil – Iron pots – Tin plates – Rag stones – Adze. Mincing knives – Cases Soap – Tubs – Paint brushes. Issued whaling gear to Mr. Brown – Mr. Prices – and Mr. Williams, Mr. Chaceland – and also provisions for 1 week to Mr. Chaceland’s gang – Employed six hands regulating provisions in store &c. Broached cask flour.
Wed. – 25th. – Employed issuing provisions to gangs – storing cargo – stowing away slops in casks, &c. – the six hands still employed.
Thurs. – 26th. – Issued whaling gear to Angas, Williams, Hedges, Chaceland & Brown – victualled 14 Māoris belonging to Mr. Chaceland and Price’s gangs for 1 week. Served out grog to same gangs – Received a quantity of flour, sugar &c. from Dublin Packet – Stored the same – Broached cask flour & beef.
Frid. – 27th. – Employed issuing stores to Tonguers [the workers who cut up the whales] – receiving and stowing away in the stores cargo from the Dublin Packet – gave Williams tea for Headsmen for Upper Fishery for 1 week.
Sat. – 28th. – Gave Black and Tandy carpenters rum for 1 week. G. Ryan, Cooper, Tea for a fortnight – Chaceland’s gang day’s grog – Boat gear to hedges, Angas and Chaceland – 2 hands employed rolling cargo from Dublin Packet into store, &c.
Sun. – 29th. – Gave Mr. Price 17 fathoms rope for Middle Fishery – Mr. Chaceland tobacco – Mr. Cureton 1 breaker of oil & 1 axe for Middle Fishery. Mr. Angas 2¼ yds of duck fisher, Muckleroy & Davis one lot grog each. Mr. Price received 2 days allowance grog for his gang – 1 Māori employed cleaning bone.
Mon. – 30th. – Mr Chaceland, Mr Williams drew whaling gear from store. Issued 1 week’s provisions to Mr. Cureton & Abbot received 16 casks flour from Dublin Packet 2 labourers employed Fisher and Davis. Mr Price drew 2 days’ grog 2 for his gang.
Tues. – May 1st. – Issued Provisions to Mr. Chaceland’s Gang and to Mr. Cureton’s Boat Crew of 5 Hands – Employed filling pork casks with fresh pickle, stowing flour in store, and serving out slops to Manuel – Black etc – Broached cask beef.
May 2nd. – Served out provisions to Mr. Price’s Gang of 25 White People and 7 Māoris for 1 week – slops to Davis and Hewit, Brown & O’Donnel – Provisions to Roberts. Received a quantity of whale bone from the Tonguers of Middle Fishery – filled up pork cask with pickle – gave Māoris their tobacco at the Middle Fishery for 2 weeks – to Mr. Chaceland’s Māori 1 week’s tobacco – Broached 1 keg & 1 Hhd [Hogshead?] of flour 1 tierce [a tierce of pork was around 136 kg of pickled pork] pork – Shipped 6 casks oil.
Thurs. – 3rd – Issued provisions to 7 Māoris in Mr. Chaceland’s gang for 5 days – & 2 bone cleaners – also 2 week’s tobacco – Employed drawing off liquor – putting slops in casks – setting stove &c. Shipped 6 casks oil.
Fri. – 4th – Issued provisions to Isaac – for 1 Week – 1 piece pork for House – finished setting stove, made Carey and Russel’s accounts out. 3 bone cleaners employed.
Sat. – 5th. – Issued Slops to Manuel & Russel, and provisions to house – Grog to Upper Fishery etc & 3 bone cleaners.
Sun. – 6th. – Received 1 head of bone from Upper Tonguers. Issued slops &c. – dined on board the Dublin Packet. – Grog to upper gang and three bone cleaners.
Mon. – 7th. – 6 bone cleaners employed – Cooper at day’s work. Issued grog to Chaceland’s gang and bone cleaners – Gave slops to 4 of bone cleaners. – Provisions to House – Settled John Carey’s account – 3 glasses grog to Mucleroy, Davis, Fisher and Isaac each.
Tues. – 8th. – Issued provisions to Price & Chaceland’s gang – to 22 Māoris – Coe at his own work, stowed cleaned bone in store. Shipped 4 casks oil – Slops to Fowler – Broached 2 casks flour 1 cask pork – Provisions to House – Geo. Gray’s grog stopped by order of Chaceland, carpenter’s by Doctor – Cooper headed up cured fish.
Wed. – 9th. – 6 bone cleaners employed – Grog to Do [ditto] and Chaceland’s gang. Issued provisions to coopers and carpenters and 1 piece beef to House. Shipped oil on board schooner Dublin Packet. Blacked tanks and rolled 1 up into yard to keep bone in. Broached cask beef.
Thurs. 10th. – 7 bone cleaners employed. Issued grog to them and Chaceland’s gang. Provisions to House – Employed regulating accounts, &c.
Fri. 11th. – Issued provisions to Mucleroy and Isaac – House 1 piece pork – Black, Ryan and Tandy tea for 1 Week – Slops to two Māoris – Tobacco to people. Making people’s bills out. 6 bone cleaners employed – Geo. Smith’s grog stopped by order of Doctor. Stowed cleaned bone in loft – Mr Philippin one steer oar.
Sat. – Gave Mr. Williams tea for four for 1 Week – Grog to Chaceland’s gang. – 6 bone cleaners employed – finished cleaning bone – Tyro [Taiaroa] – Grog from this date.
Sun. – 13th. – 7 Māoris employed repairing fences – brought spare boat from fishery to be repaired – 14 lbs. flour for House, 1 lb. tea 2 pieces pork – 1 keg to Mr. Price.
Mon. – 14th. – 5 Māoris employed repairing shed for cooper – Employed making out people’s bills – issuing provisions &c. – Sent two casks peas, two casks flour aboard the French vessel “La Fawn” [“Faune” a French whaling ship that called in twice to Ōtākou in 1838] in exchange for rope, &c.
Tues. – 15th. – Issued provisions to 35 hands in Mr. Price’s Gang, to 28 people in Mr. Chaceland’s gang – to 6 Māoris bone cleaners – Provisions to Davis and Fisher – Slops to people – received four casks beef from the French vessel “La Fawn” – Māoris as yesterday – Gave Captain Bruce 20 lbs rivets – Whaling gear to Price, Hedges, Angas and Williams.
Wed. – 16th. – Provisions to carpenters and cooper – Grog to Chaceland’s gang & Māori bone cleaners – 6 – Employed drawing of spirits – 20 gallons – regulating store, &c. – returned the four casks beef received yesterday from on board “La Fawn” – and got in lieu 3 casks pork.
Thurs. – 17th. – Employed repairing fences – Cleaning bone 6 Māoris – Gave Captain Wells 4½ bundles hooping. Settled Mr. J. Russel’s account in slops – issued provisions to House – Grog to gang – Māori and coopers – Cooper made 2 Piggin, 1 Buckey, 1 Keg.
Fri. – 18th. 6 Māoris employed making a fence between the beach and Cooper’s Workshop with the Whales Head Bones – Making foxes to tie up bone with – Issued grog to Chaceland’s gang – coopers, carpenters and Māoris. Drew off twenty two gallons spirits for Captain Wells.
Sat. – 19th. 6 Māoris employed as yesterday – issued provisions to House – Mr. Weller shooting on the other shore with Captain Wells – Issued grog to Chaceland’s gang, Māoris, coopers, carpenters, cooks &c. Williams 1 pulling oar.
Sun. – 20th. – 6 Māoris employed fetching wood for fence, bringing bones from Upper Fishery, &c. – Gave the Captain Of “La Fawn” 25 pounds of 30 hundred hooping to repair his rudder. Issued provisions to House – dined on board the Dublin Packet.
Mon. – 21st. – Māoris as yesterday – Issued provisions to House – Grog to Chaceland’s gang, coopers, carpenters, cooks &c. Received ½ head bone from Upper Tonguers.
Tues. – 22nd. – Issues Provisions to Middle and Upper Gangs – Do. To 6 Māori bone cleaners – Received the other half head bone from Upper Tonguers – vice from French vessel – Māoris employed removing sand bank abrest carpenter’s House.
Wed. – 23rd. – Provisions issued to cooper and carpenters – to Mr Brown for Pūrākaunui &c. – 4 Māoris employed cleaning bone and received 30 bundles of shooks from the Dublin Packet – 2 Māoris left without permission.
Thurs. – 24th – Provisions to House. 5 Māoris employed cleaning bone – repairing road – fetching water &c. Issued slops to Chaceland – 1 Māori not returned – Drew off ten gallons spirits.
Fri. – 25th – Provisions to House. Issued slops etc to Mr Phillipine – Māoris employed making spun yarn for bone, bring bone from the Upper Fishery – to repair fence &c. – The Māori returned to his duty.
Sat. – 26th. – Provisions to House. 6 Māoris employed repairing cooper’s house, making fence, bring earth to repair road etc. – Mr Chaceland lost 40 fathom Whale Line & iron – Steward of Dublin Packet repairing the bellows – Killed a pig.
Sun. – 27th. – Sent three Māoris back to Mr Brown who had run away from Pūrākaunui – Māoris employed fetching grass for cooper’s house and fence – grog to gang, &c.
Mon. – 28th. – Issued slops to Davis & Fisher – Drew off 30 gallons spirits for Mr Brown – 6 Māoris employed as yesterday – set the bellows up.
Tues. – 29th. – Issued provisions to Price’s & Chaceland’s Gangs – to 6 Māori labourers – Māoris employed cleaning up bone – Quin once of Mr Price’s gang fell from a cliff and killed himself.
Wed. – 30th. – Issued provisions to Black, Tandy and Ryan – to Mr Brown 240 lbs sugar 30 gallons rum 6 pounds tea & 100 figs of tobacco – to Māori cook of Big House – 6 natives employed cleaning bone, repairing cooper’s house, building fence &c. Buried Quin in the ground behind Carpenter’s Workshop.
Thurs. – 31st – Had the honour of being threatened by Mr Angas that he would smash my bloody head – cautioned him against so doing – and told him if he did not succeed I should not make a light business of it – 6 Māoris employed as yesterday – sent provisions from Dublin Packet to Pūrākaunui – Grog to gangs, &c.
Fri. June 1st. – 6 Māoris employed cleaning bone, rolling provisions to beach for Tyro [local Chief Taiaroa] to take to Pūrākaunui, but did not go – scraping boat – finishing making fence by Cooper’s house – received 400 blades bone from Pūrākaunui by Tyro and Jackey White [local Chief Karetai] – as also a receipt from Mr Brown for having received 14 casks provisions – issued 30 lbs sugar to Dublin Packet.
Sat. – 2nd – 6 Māoris employed repairing chimney of cooper’s house, cleaning bone, scraping boat &c. Issued provisions to 1 Māori for Mr Cureton’s boat – clothes etc. – Mr A and – C. tea. Stopped Māori’s grog for not coming earlier in the morning.
Sun. – 3rd – 5 Māoris employed cleaning bone – Issued provisions to House – Tea to Mr Williams and Hedges. Slops to Fowler and Chaceland – Mr Weller out shooting and dined on board the Dublin Packet.
Mon. – 4th – Issued slops &c. to Mr Manuel & provisions to house. Māoris employed as yesterday.
Tues. – 5th Issued provisions to Price’s and Chaceland’s gang – To 6 Māoris – Bone cleaners. Māoris employed cleaning bone, rolling water up from and bringing lie [lye?] from tryworks – issued whaling gear to Chaceland – provisions to David and Fisher, and Mucleroy and Isaac Porter.
Wed. – 6th. – Issued provisions to cooper and carpenters – whaling gear to Mr Cureton, 6 Māoris employed cleaning bone.
Thurs. – 7th. – Māoris employed cleaning bone – sent three Māoris away in boat to Hobart town fishery with Lowe to bring up plank for to make a trough for lie [lye] – to clean bone in. Engaged a cooper of the name – John Clarke – to make casks at the rate of 20/- per ton on labour at the rate of £6 per month.
Fri. – 8th. – Māoris employed as yesterday – issued whaling gear to Mr Manuel Goombs and tobacco to himself and boat’s crew – also 1 lb of tea to Mr Brind – received 2 kegs 1 line tub and 1 old repaired piggin from cooper.
Sat. – 9th – Māoris employed clearing bone – shipped a Frenchman from the ship “La Fawn” of the name Victor Hobé – Issued provisions to the same and to John Clarke (Cooper) Tea to Mr Williams and Hedges – Carpenter made trough for bone – Issued tobacco to Roberts – Williams, &c.
In preparing this blog I consulted the following sources on Harwood family history, the Wellers, Ōtākou and whaling:
http://www.toituosm.com/collections/smith-gallery/wall-1/octavius-harwood
https://ngataonga.org.nz/blog/nz-history/octavius-francis-harwood-a-journey-of-family-discovery/
https://teara.govt.nz/en/biographies/1w13/weller-edward
http://www.toituosm.com/collections/smith-gallery/wall-1/edward-weller
Church, Ian (ed), Gaining a Foothold : Historical Records of Otago’s Eastern Coast, 1770-1839, Friends of the Hocken Collections, 2008.
Church, Ian, Opening the Manifest on Otago’s Infant Years, Shipping Arrivals and Departures Otago Harbour and Coarst 1770-1860, Otago Heritage Books 2001
Harwood, Mac, Octavius Harwood, Titopu, Piro, Janet Robertson, published by Mac Harwood, Upper Takaka, 1989.
King, Alexandra, The Weller’s whaling station : the social and economic formation of an Otakou community, 1817-1850. https://ourarchive.otago.ac.nz/handle/10523/5533F
Tod, Frank, Whaling in Southern Waters, published by Frank Tod1982
West, Jonathon, The Face of Nature : An Environmental History of the Otago Peninsula, Otago University Press, 2017













 Are you a machine knitter, cat fancier, Ruritanian folk dancer, Chrysler restorer, lace maker, ship wreck welfare specialist or antique bottle collector? If so, then you will be interested in some of the approximately 3145 club and society periodicals located in the Hocken Journals collection. We hold many different types of publications produced by clubs and societies including; meeting minutes, newsletters, rule books, annual reports and accounts. These periodicals come from all over New Zealand, the Pacific and Antarctica and cover a broad range of topics.
Are you a machine knitter, cat fancier, Ruritanian folk dancer, Chrysler restorer, lace maker, ship wreck welfare specialist or antique bottle collector? If so, then you will be interested in some of the approximately 3145 club and society periodicals located in the Hocken Journals collection. We hold many different types of publications produced by clubs and societies including; meeting minutes, newsletters, rule books, annual reports and accounts. These periodicals come from all over New Zealand, the Pacific and Antarctica and cover a broad range of topics.